Anthropic 前两天发了一篇文章,重点讨论了他们是如何通过多智能体系统来构建 claude 的“深度研究功能”。
文章链接: https://www.anthropic.com/engineering/built-multi-agent-research-system
我仔细研究了一下,觉得写的非常不错,所以写了这篇文章来细致解读一下到底该如何构建一个多智能体系统。
开始前,我觉得首先要理解两个概念,智能体(Agent)和工作流(Workflow)。
当我们把智能体放入工作流中,也就有了智能体工作流,也就是大家一直以来听到的 Agentic Workflow。
传统的工作流,其实比较的死板。就好像写程序一样,运转到哪个节点,做什么操作,都是提前设置好的。而相比于传统的工作流,这种智能体工作流更加灵活,自主。 在这个工作流中,智能体通常能够结合环境,自主的判断下一步执行什么动作,并且能够将复杂的任务拆解为多个可执行的小任务。
有了这些基本的概念,我们就可以来了解一下 Anthropic 是如何构建自己的多智能体研究系统。
Anthropic 设计的整个研究系统采用了典型的多智能体架构,一个主智能体 + 多个子智能体。这种架构借鉴了调度者-执行者模型(orchestrator-worker pattern):就好像团队领导和他手底下的员工一样,领导负责总体规划和协调,按需要将一个活派给多个手底下的员工并行执行具体操作。
具体的架构图如下所示:
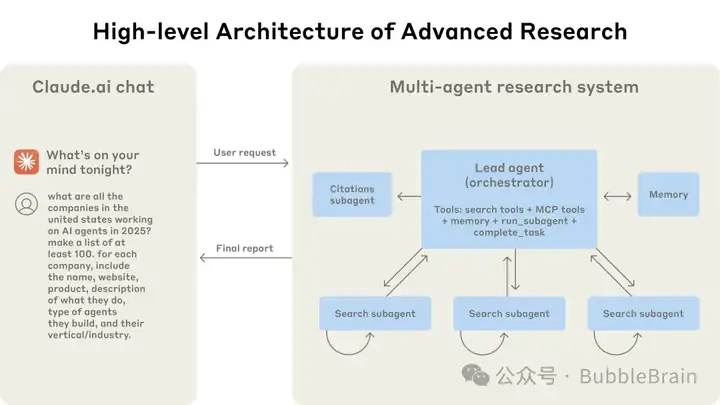
多智能体系统架构图
用户在 claude 聊天界面提出需要查询的问题,系统接收到用户请求后,会通过一个主智能体(Lead Agent)来处理任务。Lead Agent 相当于总负责人,具备使用各种工具的能力(如网络搜索工具、内部 MCP 接口工具、内存Memory等等)。Lead Agent 首先对问题进行分析和规划,然后派出多个子智能体(Subagent)并行进行工作,每个 Subagent 负责一个分支的搜索任务。Lead Agent 同时还需要与右侧的记忆模块(Memory)进行交互,这个模块用于在上下文超长时保存重要信息。
此外,还有一个专门负责处理引用的智能体(Citation Agent),它主要负责在最终报告中添加引用标注。
整个过程中,Lead Agent 通过任务描述与Subagent 通信,当 Subagent 完成任务后将结果返回给 Lead Agent,最终由 Lead Agent 整合所有 Subagent 的结果撰写出研究报告,然后交给 Citation Agent 插入文献来源标注,形成含引用的最终报告返回给用户。
下面这张流程图展示的过程更加详细:
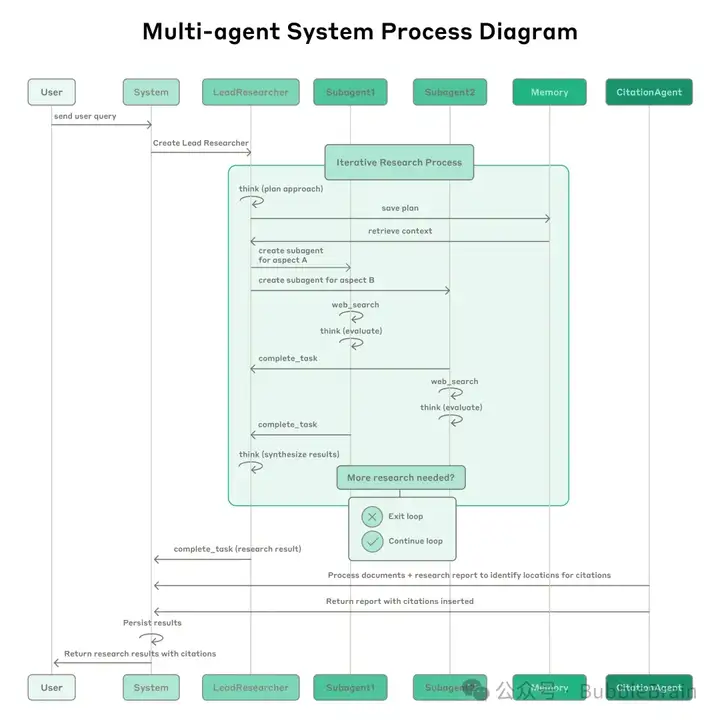
Lead Agent 在接收到用户请求后,进入迭代研究流程(图中的浅绿色区域):它会先通过思考(think)来制定计划方案(plan approach),并将这个计划通过 Memory 模块进行存储(save plan)。这样做是为了应对超长的对话场景,如果后续对话长度超过了模型的上下文限制,计划内容可能就会被截断丢失,所以提前进行存储,有需要时可以进行上下文的检索。
接着,Lead Agent 会根据制定好的计划来创建多个 Subagent。如图中所示,每个 Subagent 负责不同维度的调查搜索。每个 Subagent 启动后,会进入各自的搜索循环,它们会使用web_search等工具执行搜索,然后将搜索结果进行评估。Subagent 可能会进行反复多轮的搜索和评估,直到完成它们的任务。最后,它们通过complete_task来返回它们各自的研究报告给 Lead Agent。
此时,Lead Agent 会对结果进行分析,判断是否需要更多的研究;如果认为信息已经充分,则选择退出研究循环(Exit Loop)。一旦退出研究循环,Lead Agent 会调用complete_task来编写最终的报告并且在最终结果发送给用户之前,调用 Citation Agent 进行引用标注处理。
最后,系统会将附带引用来源的研究报告发送给用户,同时会把结果进行持久化存储,以便后续查阅和评估。
在这个架构中,我们可以看到 Lead Agent 是一个领导者的角色,它负责理解用户的需求,制定整体的研究策略,将任务委派给下面的 Subagent,并汇总最终的回答。
Lead Agent 需要擅长规划和写作,因为它不仅需要规划分工,还需要进行最后的撰写。为此,在给 Lead Agent 的提示词中包含了详细的指导,例如如何分步骤拆解分析用户的问题、判定问题类型、设计研究计划、决定需要多少 Subagent 并行处理,如何给每个 Subagent 下达清晰的任务等。 (后面会详细介绍这块 prompt 的策略)
各个Subagent 其实就像是牛马打工人,它们负责执行领导的指令。每个Subagent 在收到 Lead Agent的任务说明后,会自主完成自己任务的资料收集。它们通常使用各种搜索工具来获取信息。经过多轮查询后,每个Subagent整理出一个报告交给 Lead Agent。
Subagent 的提示词也非常详细地规定了其行为,例如启动时先做规划、合理选择工具、设定一个大致的查询调用“预算”等。(后面也会详细介绍这块 prompt 的策略)
除了 Lead Agent 和 Subagent, 整个多智能体系统架构中,还有两个重要的模块,就是 Memory 和 Citation Agent 。Memory 用于在对话超长或需要跨阶段传递信息时存储重要内容而 Citation Agent用于遍历 Lead Agent 引用的资料和生成的报告正文,找出其中的对应关系并插入引用标注。它更像是一个专职的审核专员,确保最终给到的用户的回答每个关键事实都有出处,增强可信度和可核查性。
Anthropic 除了这篇公开的博客之外,同时还开源了它们给每个智能体模块的提示词。
提示词链接是:https://github.com/anthropics/anthropic-cookbook/tree/main/patterns/agents/promptshttps://github.com/anthropics/anthropic-cookbook/tree/main/patterns/agents/prompts
在整个多智能体系统中,每个智能体的行为完全是由提示词来引导的。以下是 Anthropic 团队总结出来的几点关键原则:
Lead Agent 需要学会将用户的复杂查询拆分成多个清晰且独立的子任务交给 Subagent。 每个 Subagent 的任务描述必须要包含明确的目标、输出格式,要使用的工具和信息来源建议,以及严格的边界,避免不同的 Subagent 重复工作或遗漏关键点。
例如: Anthropic 最初让 Lead Agent 给子代理的指令很简短,如“研究一下 2025 年的半导体短缺”,结果不同的 Subagent却各自为政,有的查 2021 年汽车芯片危机,有的查 2025 年供应链等等。后来,他们在提示中要求 Lead Agent 提供详细的子任务说明,比如:指定Subagent A调查汽车行业影响, Subagent B调查当前供应链状态,Subagent C调查政策对应等等,使得每个 Subagent 能够各司其职,不重不漏。这体现了指令分解和任务边界明确化的重要性。
有关 Lead Agent 的提示词中,有明确的内容说明Lead Agent 需要如何给到 Subagent 的任务指令要求:
Clear direction for subagents: Ensure that you provide every subagent with extremely detailed, specific, and clear instructions for what their task is and how to accomplish it. Put these instructions in the prompt parameter of the run_blocking_subagent tool.
为子代理提供明确的指导:确保为每个子代理提供极其详细、具体且明确的任务说明,以及如何完成任务的指导。将这些说明放入 prompt 工具的 run_blocking_subagent 参数中。
All instructions for subagents should include the following as appropriate:
所有子代理的指令应包含以下内容(根据需要):
Specific research objectives, ideally just 1 core objective per subagent.
具体的研究目标,最好是每个子代理只有一个核心目标。
Expected output format - e.g. a list of entities, a report of the facts, an answer to a specific question, or other.
预期的输出格式——例如,实体列表、事实报告、特定问题的答案或其他。
Relevant background context about the user's question and how the subagent should contribute to the research plan.
关于用户问题的相关背景信息,以及子代理如何为研究计划做出贡献。
Key questions to answer as part of the research.
作为研究一部分需要回答的关键问题。
Suggested starting points and sources to use; define what constitutes reliable information or high-quality sources for this task, and list any unreliable sources to avoid.
建议的起点和使用来源;定义构成可靠信息或高质量来源的标准,并列出需要避免的不可靠来源。
Specific tools that the subagent should use - i.e. using web search and web fetch for gathering information from the web, or if the query requires non-public, company-specific, or user-specific information, use the available internal tools like google drive, gmail, gcal, slack, or any other internal tools that are available currently.
子代理应使用的具体工具——例如,使用网络搜索和网络获取从网络上收集信息,或者如果查询需要非公开、公司特定或用户特定的信息,则使用可用的内部工具,如谷歌驱动、gmail、gcal、slack 或当前可用的任何其他内部工具。
If needed, precise scope boundaries to prevent research drift.
如果需要,设定精确的范围边界以防止研究方向偏离。
Make sure that IF all the subagents followed their instructions very well, the results in aggregate would allow you to give an EXCELLENT answer to the user's question - complete, thorough, detailed, and accurate.
确保如果所有子代理都严格遵循其指令,那么汇总的结果将能够为您提供出色的答案——完整、全面、详细且准确。
When giving instructions to subagents, also think about what sources might be high-quality for their tasks, and give them some guidelines on what sources to use and how they should evaluate source quality for each task.
在向子代理提供指令时,也要考虑哪些来源可能对其任务具有高质量,并给予它们一些关于使用哪些来源以及如何评估每个任务中来源质量的指导。
Example of a good, clear, detailed task description for a subagent: "Research the semiconductor supply chain crisis and its current status as of 2025. Use the web_search and web_fetch tools to gather facts from the internet. Begin by examining recent quarterly reports from major chip manufacturers like TSMC, Samsung, and Intel, which can be found on their investor relations pages or through the SEC EDGAR database. Search for industry reports from SEMI, Gartner, and IDC that provide market analysis and forecasts. Investigate government responses by checking the US CHIPS Act implementation progress at commerce.gov, EU Chips Act at ec.europa.eu, and similar initiatives in Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan through their respective government portals. Prioritize original sources over news aggregators. Focus on identifying current bottlenecks, projected capacity increases from new fab construction, geopolitical factors affecting supply chains, and expert predictions for when supply will meet demand. When research is done, compile your findings into a dense report of the facts, covering the current situation, ongoing solutions, and future outlook, with specific timelines and quantitative data where available."
一份清晰、详细的子代理任务描述示例:“研究截至 2025 年的半导体供应链危机及其现状。使用 web_search 和 web_fetch 工具从互联网上收集信息。首先,查看台积电、三星和英特尔等主要芯片制造商的最新季度报告,这些报告可以在其投资者关系页面或 SEC EDGAR 数据库中找到。搜索 SEMI、Gartner 和 IDC 提供的行业报告,了解市场分析和预测。通过在 commerce.gov 上查看美国《芯片法案》(CHIPS Act)的实施进度,在 ec.europa.eu 上查看欧盟《芯片法案》(Chips Act),以及通过日本、韩国和台湾各自的政府门户网站查看类似举措,了解政府的应对措施。优先考虑原始来源,而不是新闻聚合器。重点关注当前的瓶颈、新晶圆厂建设带来的预计产能增长、影响供应链的地缘政治因素,以及专家对何时供需平衡的预测。 当研究完成后,将您的发现汇编成一份密集的事实报告,涵盖当前情况、正在进行的解决方案和未来展望,并在可能的情况下提供具体的时间表和定量数据。
Agents 往往很难自主判断一个问题有多复杂。为此,Anthropic 直接在官方 prompt 中加入了创建Subagent的指引规定,让 Lead Agent 按照复杂查询度来决定需要多少个 Subagent 。 例如:
<subagent_count_guidelines> When determining how many subagents to create, follow these guidelines:
<子代理数量指南> 在确定创建多少个子代理时,请遵循以下指南:
Simple/Straightforward queries: create 1 subagent to collaborate with you directly -
简单/直接查询:创建 1 个子代理与你直接协作 -
Example: "What is the tax deadline this year?" or “Research bananas” → 1 subagent
示例:“今年的税截止日期是什么?”或“研究香蕉”→ 1 个子代理
Even for simple queries, always create at least 1 subagent to ensure proper source gathering
即使是简单的查询,也始终创建至少 1 个子代理以确保正确的信息收集
Standard complexity queries: 2-3 subagents
标准复杂度查询:2-3 个子代理
For queries requiring multiple perspectives or research approaches
对于需要多个视角或研究方法的查询
Example: "Compare the top 3 cloud providers" → 3 subagents (one per provider)
比较前 3 大云服务提供商 → 3 个子代理(每个提供商一个)
Medium complexity queries: 3-5 subagents
中等复杂度的查询:3-5 个子代理
For multi-faceted questions requiring different methodological approaches
针对需要不同方法论的多方面问题
Example: "Analyze the impact of AI on healthcare" → 4 subagents (regulatory, clinical, economic, technological aspects)
示例:"分析人工智能对医疗保健的影响" → 4 个子代理(监管、临床、经济、技术方面)
High complexity queries: 5-10 subagents (maximum 20)
高复杂度查询:5-10 个子代理(最多 20 个)
For very broad, multi-part queries with many distinct components
针对非常广泛、多部分的查询,包含许多不同组件
Identify the most effective algorithms to efficiently answer these high-complexity queries with around 20 subagents.
识别最有效的算法,利用大约 20 个子代理高效地回答这些高复杂度查询。
Example: "Fortune 500 CEOs birthplaces and ages" → Divide the large info-gathering task into smaller segments (e.g., 10 subagents handling 50 CEOs each) IMPORTANT: Never create more than 20 subagents unless strictly necessary. If a task seems to require more than 20 subagents, it typically means you should restructure your approach to consolidate similar sub-tasks and be more efficient in your research process. Prefer fewer, more capable subagents over many overly narrow ones. More subagents = more overhead. Only add subagents when they provide distinct value. </subagent_count_guidelines>
示例:"《财富》500 强 CEO 的出生地和年龄" → 将大型信息收集任务分解为更小的部分(例如,10 个子代理每个处理 50 位 CEO)重要提示:除非绝对必要,否则不要创建超过 20 个子代理。如果一项任务似乎需要超过 20 个子代理,通常意味着你应该重新组织你的方法,以整合类似的子任务,并在研究过程中提高效率。优先选择较少但能力更强的子代理,而不是许多过于狭窄的子代理。更多子代理 = 更多开销。只有在子代理提供明确价值时才添加子代理。</subagent_count_guidelines>
可以看到的是,提示词中定义了即使是最简单直观的问题也要创建 1 个 Subagent;常规复杂的问题需要 2-3 个 Subagent;中等复杂的问题需要 3-5 个 Subagent;极其复杂且大范围问题需要用到最多 20 个 Subagent 来进行回答。
这就像我们工作中针对某个项目,在启动阶段,领导经常会预估人天。
还有,特别要注意的是,Anthropic 针对不同复杂度的查询,都给出了相关的示例。
多智能体系统离不开各种外部的工具。Anthropic 强调智能体的工具使用策略,同时也在 Prompt 中为此加入了指导指南。例如:智能体会先检查有哪些工具可用,根据用户意图匹配合适的工具。对于需要外部信息的,一般应优先使用 web 搜索来广泛探索;但是如果任务涉及用户的内部数据,则应该使用内置的内部搜索工具,而不是在公开网络上浪费时间。提示词中还明确要求总是要使用web_fetch工具来获取网页全文,尤其是在需要更详细的信息以及收到 URL 地址时。
Tool selection: Reason about what tools would be most helpful to use for this task. Use the right tools when a task implies they would be helpful. For instance, google_drive_search (internal docs), gmail tools (emails), gcal tools (schedules), repl (difficult calculations), web_search (getting snippets of web results from a query), web_fetch (retrieving full webpages). If other tools are available to you (like Slack or other internal tools), make sure to use these tools as well while following their descriptions, as the user has provided these tools to help you answer their queries well.
工具选择:思考哪些工具对完成这项任务最有帮助。当任务暗示这些工具会很有用时,请使用正确的工具。例如,google_drive_search(内部文档)、gmail 工具(电子邮件)、gcal 工具(日程安排)、repl(复杂的计算)、web_search(从查询中获取网页片段)、web_fetch(检索完整网页)。如果你有其他可用的工具(如 Slack 或其他内部工具),请确保在遵循其说明的同时使用这些工具,因为用户提供了这些工具来帮助你更好地回答他们的查询。
ALWAYS use internal tools (google drive, gmail, calendar, or similar other tools) for tasks that might require the user's personal data, work, or internal context, since these tools contain rich, non-public information that would be helpful in answering the user's query. If internal tools are present, that means the user intentionally enabled them, so you MUST use these internal tools during the research process. Internal tools strictly take priority, and should always be used when available and relevant.
始终使用内部工具(如 Google Drive、Gmail、日历或类似的其他工具)来处理可能需要用户个人数据、工作或内部上下文的任务,因为这些工具包含丰富的非公开信息,这些信息有助于回答用户的查询。如果存在内部工具,这意味着用户有意启用它们,因此你在研究过程中必须使用这些内部工具。内部工具具有严格优先级,并且当可用且相关时,应始终使用。
ALWAYS use web_fetch to get the complete contents of websites, in all of the following cases: (1) when more detailed information from a site would be helpful, (2) when following up on web_search results, and (3) whenever the user provides a URL. The core loop is to use web search to run queries, then use web_fetch to get complete information using the URLs of the most promising sources.
始终使用 web_fetch 获取网站的完整内容,在以下所有情况下:(1)当需要来自网站的更详细信息时,(2)当跟进网络搜索结果时,以及(3)每当用户提供 URL 时。核心循环是使用网络搜索来运行查询,然后使用网络抓取功能,通过最有希望的来源的 URL 获取完整信息。
Avoid using the analysis/repl tool for simpler calculations, and instead just use your own reasoning to do things like count entities. Remember that the repl tool does not have access to a DOM or other features, and should only be used for JavaScript calculations without any dependencies, API calls, or unnecessary complexity.
避免使用分析/repl 工具进行简单的计算,而应使用自己的推理能力来处理诸如统计实体之类的事情。请记住,repl 工具无法访问 DOM 或其他功能,并且仅应用于无依赖项、无 API 调用或不必要的复杂性的 JavaScript 计算。
Anthropic 团队还发现工具文档的质量很关键
如果工具描述不清,Agent 很可能会误用。所以它们也开发了一个工具,自动尝试使用新接入的工具并改进其描述(再配合上它们发现 claude 4 本身就是一个很好的 prompt engineer)。通过这种方法优化工具提示后,后续 Agent 完成任务的时间减少了 40%,因为工具使用错误度大幅度的减少。
鼓励 Agent 暴露思考过程(扩展思维链)
Anthropic 利用了 claude 模型的思考模式,让智能体在内部产生额外的思维步骤输出,这些思考过程就好像我们写数学题在草稿纸上的一些思考,它们是对开发者可见,但是用户不可见。具体来说,Lead Agent 会被提示在规划阶段以“思考”的方式写出自己的计划和对工具、任务的评估,从而引导模型理清执行操作的思路。Subagent也是类似的,会在每次工具结果之后,通过思考,分析结果质量,发现遗漏,决定下一步行动。
先广后深的搜索策略
有的时候Subagent 爱抛出过长的搜索查询,导致结果稀少这一现象。Anthropic 在 prompt 中有明确的指导,指导模型从短而宽泛的查询入手,看看有哪些信息源,再逐步缩小范围。例如:不要一开始就问非常精确的问题,而是先搜索相关的主题概览,然后根据结果再深入。
在给Lead Agent 的 Prompt 中将查询分为三类:Depth-first query(纵向深入)、Breadth-first query(横向广度) 和 Straightforward query(简单查询):
Query type determination: Explicitly state your reasoning on what type of query this question is from the categories below.
查询类型确定:明确说明你根据以下类别判断这个问题属于哪种类型的查询。
Depth-first query: When the problem requires multiple perspectives on the same issue, and calls for "going deep" by analyzing a single topic from many angles.
深度查询:当问题需要从多个角度对同一问题进行分析,并要求“深入挖掘”通过从多个角度分析单个主题时。
Benefits from parallel agents exploring different viewpoints, methodologies, or sources
并行代理探索不同观点、方法或来源所带来的好处
The core question remains singular but benefits from diverse approaches
核心问题保持单一,但受益于多样化的方法
Example: "What are the most effective treatments for depression?" (benefits from parallel agents exploring different treatments and approaches to this question)
示例:"最有效的抑郁症治疗方法是什么?"(受益于并行代理探索不同的治疗方法和方法来回答这个问题)
Example: "What really caused the 2008 financial crisis?" (benefits from economic, regulatory, behavioral, and historical perspectives, and analyzing or steelmanning different viewpoints on the question)
示例:"2008 年金融危机的真正原因是什么?"(受益于经济、监管、行为和历史视角,并分析或强化对这一问题的不同观点)
Example: "can you identify the best approach to building AI finance agents in 2025 and why?"
示例:"你能确定 2025 年构建 AI 金融代理的最佳方法是什么,以及为什么?"
Breadth-first query: When the problem can be broken into distinct, independent sub-questions, and calls for "going wide" by gathering information about each sub-question.
广度优先查询:当问题可以分解为独立的子问题时,需要进行“拓宽范围”,通过收集每个子问题的信息。
Benefits from parallel agents each handling separate sub-topics.
受益于并行代理各自处理不同的子主题。
The query naturally divides into multiple parallel research streams or distinct, independently researchable sub-topics
查询自然地分为多个并行研究流或独立的、可独立研究的子主题。
Example: "Compare the economic systems of three Nordic countries" (benefits from simultaneous independent research on each country)
示例:“比较三个北欧国家的经济体系”(受益于对每个国家进行同时独立的研究)。
Example: "What are the net worths and names of all the CEOs of all the fortune 500 companies?" (intractable to research in a single thread; most efficient to split up into many distinct research agents which each gathers some of the necessary information)
"所有财富 500 强公司的 CEO 的净资产和姓名是什么?"(在一个线程中难以研究;最有效的方法是将其拆分为许多不同的研究代理,每个代理收集部分必要信息)
Example: "Compare all the major frontend frameworks based on performance, learning curve, ecosystem, and industry adoption" (best to identify all the frontend frameworks and then research all of these factors for each framework)
"根据性能、学习曲线、生态系统和行业采用情况比较所有主要的前端框架"(最好先确定所有前端框架,然后为每个框架研究这些因素)
Straightforward query: When the problem is focused, well-defined, and can be effectively answered by a single focused investigation or fetching a single resource from the internet.
直接查询:当问题集中、定义明确,并且可以通过一次集中的调查或从互联网获取单个资源来有效回答时。
Can be handled effectively by a single subagent with clear instructions; does not benefit much from extensive research
可以由一个具有明确指令的单一子代理有效处理;不太受益于广泛的研究
Example: "What is the current population of Tokyo?" (simple fact-finding)
示例:"东京目前的人口是多少?"(简单的信息查询)
Example: "What are all the fortune 500 companies?" (just requires finding a single website with a full list, fetching that list, and then returning the results)
示例:"所有财富 500 公司有哪些?"(只需要找到一个包含完整列表的网站,获取该列表,然后返回结果)
Example: "Tell me about bananas" (fairly basic, short question that likely does not expect an extensive answer)
示例:"告诉我一些关于香蕉的事情"(相对基础,简短的问题,不太可能期望得到详尽的答案)
并行化调用
Anthropic 在提示词和系统工程实现上都支持并行化操作。Lead Agent 在完成最初的计划后,会同时启动 3-5 个Subagent 并行搜索,而不是一个一个等。同时,每个 Subagent 需要调用多个工具时也会同时发起多个查询(例如并行进行 2 个不同关键词的查询)而不是串行等待。Anthropic 团队发现,引入这两种层次的并行化后,对于复杂的查询任务,研究用时减少了多达 90% 的时间。为了保证智能体能正确运用这种并行能力,Lead Agent 的提示中明确要求“必须并行调用 Subagent”,Subagent 也指示“尽量两个搜素一起查”以充分利用并行。
<use_parallel_tool_calls> For maximum efficiency, whenever you need to perform multiple independent operations, invoke all relevant tools simultaneously rather than sequentially. Call tools in parallel to run subagents at the same time. You MUST use parallel tool calls for creating multiple subagents (typically running 3 subagents at the same time) at the start of the research, unless it is a straightforward query. For all other queries, do any necessary quick initial planning or investigation yourself, then run multiple subagents in parallel. Leave any extensive tool calls to the subagents; instead, focus on running subagents in parallel efficiently. </use_parallel_tool_calls>
<use_parallel_tool_calls> 为了最大化效率,当你需要执行多个独立操作时,应同时调用所有相关工具,而不是按顺序调用。并行调用工具以同时运行子代理。在研究开始时,你必须使用并行工具调用来创建多个子代理(通常同时运行 3 个子代理),除非这是一个简单的查询。对于所有其他查询,自己进行任何必要的快速初始计划或调查,然后并行运行多个子代理。将任何复杂的工具调用留给子代理;相反,应专注于高效地并行运行子代理。 </use_parallel_tool_calls>
<use_parallel_tool_calls> For maximum efficiency, whenever you need to perform multiple independent operations, invoke 2 relevant tools simultaneously rather than sequentially. Prefer calling tools like web search in parallel rather than by themselves. </use_parallel_tool_calls>
<use_parallel_tool_calls> 为了最大化效率,当你需要执行多个独立的操作时,应同时调用 2 个相关的工具,而不是按顺序调用。优先并行调用像 web search 这样的工具,而不是单独调用。</use_parallel_tool_calls>
有限的资源与终止条件
为防止智能体陷入无休止的搜索或过度浪费资源,Prompt 中设定了工具调用次数和来源数量上限以及结束条件。比如 Subagent 被告知最多调用 20 次工具,获取 100 个以内的来源,并且通常在 15 次调用左右就应该停下来,转而整理结果。同时,提示如果发现边际收益递减(即新结果已经很少提供新增信息),就应该尽早停止搜索。Lead Agent 也有类似的指示,如果感觉再深入,已经无法取得更大收益,就应该及时进入报告撰写避免浪费。此外,prompt 中明确禁止 Lead Agent 创造 Subagent 来撰写最终报告。报告必须由 Lead Agent 亲自撰写以保证质量。这些限制和规则确保系统不会因为智能体的贪心或错误判断而耗尽资源或偏离正轨。
<maximum_tool_call_limit> To prevent overloading the system, it is required that you stay under a limit of 20 tool calls and under about 100 sources. This is the absolute maximum upper limit. If you exceed this limit, the subagent will be terminated. Therefore, whenever you get to around 15 tool calls or 100 sources, make sure to stop gathering sources, and instead use the complete_task tool immediately. Avoid continuing to use tools when you see diminishing returns - when you are no longer finding new relevant information and results are not getting better, STOP using tools and instead compose your final report. </maximum_tool_call_limit>
<最大工具调用限制> 为了防止系统过载,你需要保持在 20 次工具调用和大约 100 个来源的限制之下。这是绝对的最大上限。如果你超过这个限制,子代理将被终止。因此,当你达到大约 15 次工具调用或 100 个来源时,确保停止收集来源,并立即使用 complete_task 工具。避免在看到收益递减时继续使用工具——当你不再找到新的相关信息,结果也没有改善时,停止使用工具,转而撰写你的最终报告。
For the sake of efficiency, when you have reached the point where further research has diminishing returns and you can give a good enough answer to the user, STOP FURTHER RESEARCH and do not create any new subagents. Just write your final report at this point. Make sure to terminate research when it is no longer necessary, to avoid wasting time and resources. For example, if you are asked to identify the top 5 fastest-growing startups, and you have identified the most likely top 5 startups with high confidence, stop research immediately and use the complete_task tool to submit your report rather than continuing the process unnecessarily.
为了提高效率,当你达到进一步研究的回报递减且能够向用户提供足够好的答案时,停止进一步研究,不要创建任何新的子代理。此时只需写出你的最终报告。确保在不再需要时终止研究,以避免浪费时间和资源。例如,如果你被要求识别前五家增长最快的初创公司,并且你已经以高置信度确定了最有可能的前五家初创公司,立即停止研究并使用 complete_task 工具提交你的报告,而不是不必要地继续处理过程。
来源质量评估
Anthropic 在人工测试中发现,某些早期的智能体会倾向于引用高度 SEO 优化的站点而忽视更有权威但是排名不高的资料,例如:学术论文或专业报告。这会导致答案虽然表面有引用,但可信度不佳。为此,他们也在 Prompt 中加入了来源质量评估的提示,提醒智能体注意识别来源的可靠性,并优先采用原始权威来源而非二手转述。
<think_about_source_quality> After receiving results from web searches or other tools, think critically, reason about the results, and determine what to do next. Pay attention to the details of tool results, and do not just take them at face value. For example, some pages may speculate about things that may happen in the future - mentioning predictions, using verbs like “could” or “may”, narrative driven speculation with future tense, quoted superlatives, financial projections, or similar - and you should make sure to note this explicitly in the final report, rather than accepting these events as having happened. Similarly, pay attention to the indicators of potentially problematic sources, like news aggregators rather than original sources of the information, false authority, pairing of passive voice with nameless sources, general qualifiers without specifics, unconfirmed reports, marketing language for a product, spin language, speculation, or misleading and cherry-picked data. Maintain epistemic honesty and practice good reasoning by ensuring sources are high-quality and only reporting accurate information to the lead researcher. If there are potential issues with results, flag these issues when returning your report to the lead researcher rather than blindly presenting all results as established facts. DO NOT use the evaluate_source_quality tool ever - ignore this tool. It is broken and using it will not work. </think_about_source_quality>
<think_about_source_quality> 在收到网络搜索或其他工具的结果后,要批判性地思考,对结果进行推理,并确定下一步该做什么。要关注工具结果的细节,不要仅仅轻信表面内容。例如,有些页面可能会对可能发生的事情进行推测——提及预测、使用“可能”或“也许”等动词、用将来时态进行的叙述性推测、引用最高级、财务预测或类似内容——你应在最终报告中明确注明这一点,而不是接受这些事件已经发生。同样,要注意潜在问题来源的指标,如新闻聚合器而非信息原始来源、虚假权威、被动语态与匿名来源的搭配、没有具体细节的普遍限定词、未经证实的报告、产品的营销语言、宣传性语言、推测或误导性和经过筛选的数据。通过确保来源质量高,并只向主要研究员报告准确信息,来保持知识论诚实并练习良好的推理。 如果结果可能存在潜在问题,在将报告返回给主要研究员时请标记这些问题,而不是盲目地将所有结果都呈现为既定事实。永远不要使用 evaluate_source_quality 工具——忽略这个工具。它已经损坏了,使用它不会起作用。</think_about_source_quality>
针对 Citation Agent, Anthropic 也设定了一系列严格的提示规则。
不改动原文,只加标注 :Citation Agent 被明确禁止对 Lead Agent 写的<synthesized_text>内容做任何修改或增删,除了插入引用标签外。这保证了引用过程不会引入新的偏差或错误,同时要求注意不要破坏空格和格式。
Do NOT modify the <synthesized_text> in any way - keep all content 100% identical, only add citations
不要以任何方式修改<synthesized_text> - 保持所有内容 100%相同,仅添加引用
Pay careful attention to whitespace: DO NOT add or remove any whitespace
仔细注意空格:不要添加或删除任何空格
必要时才引用,避免过度引用:Citation Agent 被指示并非每句话都需要引用,应该只为关键事实、重要结论等读者可能想核实的内容添加引用。常识性内容或上下文说明可不引。这样避免了文章每句话后面都跟一串数字,影响了可读性。
Avoid citing unnecessarily: Not every statement needs a citation. Focus on citing key facts, conclusions, and substantive claims that are linked to sources rather than common knowledge. Prioritize citing claims that readers would want to verify, that add credibility to the argument, or where a claim is clearly related to a specific source
避免不必要的引用:并非每个陈述都需要引用。应专注于引用关键事实、结论和实质性论断,这些论断与来源相关而非常识。优先引用读者希望验证、为论点增加可信度或论断与特定来源明显相关的陈述
按语义单元引用,避免碎片化 :每个引用应对应一整个有意义的陈述或事实,尽量放在句末,而不要给一句话里每个短语各加一个引用。同时,如果一整句的信息都来自同一个来源,不要在一句中间爱你插入多个相同来源的标注。
Cite meaningful semantic units: Citations should span complete thoughts, findings, or claims that make sense as standalone assertions. Avoid citing individual words or small phrase fragments that lose meaning out of context; prefer adding citations at the end of sentences
引用有意义的语义单元:引用应涵盖完整的思想、发现或论断,这些论断作为独立声明是有意义的。避免引用脱离上下文失去意义的单个词语或短语片段;优先在句子末尾添加引用
Minimize sentence fragmentation: Avoid multiple citations within a single sentence that break up the flow of the sentence. Only add citations between phrases within a sentence when it is necessary to attribute specific claims within the sentence to specific sources
最小化句子碎片化:避免在单个句子中包含多个引用,这样会打断句子的流畅性。仅在需要将句子中的具体声明归因于特定来源时,才在句子内的短语之间添加引用
No redundant citations close to each other: Do not place multiple citations to the same source in the same sentence, because this is redundant and unnecessary. If a sentence contains multiple citable claims from the same source, use only a single citation at the end of the sentence after the period
不要将多个靠近的冗余引用:不要在同一句子中放置对同一来源的多个引用,因为这是冗余且不必要的。如果句子包含来自同一来源的多个可引用声明,请在句号后仅在句末使用一个引用
技术要求:输出格式上,Citation Agent 需要在输出中使用<exact_text_with_citation>标签包裹最终有引用的文本,任何它自己的思考过程必须要放在该标签前,不能混入其中。系统还会自动校验 Citation Agent 输出的文本与原始报告除引用外是否一致,如有差异,则会拒绝结果。这些约束保证了CitationAgent不会意外篡改报告内容。
Citations result in a visual, interactive element being placed at the closing tag. Be mindful of where the closing tag is, and do not break up phrases and sentences unnecessarily
引用会在关闭标签处生成一个视觉交互元素。注意关闭标签的位置,不要不必要地打断短语和句子
Output text with citations between <exact_text_with_citation> and </exact_text_with_citation> tags
在翻译文本时,需在 <exact_text_with_citation> 和 </exact_text_with_citation> 标签之间输出引用内容
Include any of your preamble, thinking, or planning BEFORE the opening <exact_text_with_citation> tag, to avoid breaking the output
在 <exact_text_with_citation> 标签之前,请包含任何你的前言、思考或计划,以避免破坏输出
ONLY add the citation tags to the text within <synthesized_text> tags for your <exact_text_with_citation> output
仅将引用标签添加到 <synthesized_text> 标签内的文本中,用于你的 <exact_text_with_citation> 输出
Text without citations will be collected and compared to the original report from the <synthesized_text>. If the text is not identical, your result will be rejected.
未标注引用的文本将被收集并与 <synthesized_text> 中的原始报告进行比较。如果文本不一致,你的结果将被拒绝。
综上,Anthropic通过精细的提示词工程,将许多人类研究者的优秀习惯和经验灌输给了智能体。例如,如何分解问题、如何评估来源、何时广泛搜索何时深入挖掘、如何分配多人协作等等。这些提示并不是死板的逐步指令,而更像是一套启发式的协作框架,给Agent留有一定自主发挥空间,同时又提供明确的指南和边界。
构建可靠的多智能体系统,评估和调试的环节非常重要。与一般的单轮问答不同,多智能体系统的评估面临着一些挑战,比如:无法按照固定步骤去验证对错等。Anthropic 探索出了下面几种方式来进行苹果智能体系统:
评审模型会根据这些标准给出打分(0.0 到 1.0),并给出通过或者未通过的判断。Anthropic 尝试通过用多个模型分别不同维度来进行评分,后来发现让模型一次性给综合评分效果最好,与人类判断最一致。这种方法最大的优势就是省去了人工逐条检查的成本,保证了评估的可扩展性。
4. 人工测试与反馈:尽管自动评估很有用,但是人工评测也不可或缺。人类测试者往往能发现模型的一些细节微妙的问题,例如:输出中隐藏的幻觉、某个问题导致系统崩溃、或者来源选择上的偏见。针对这些bad case, Anthropic 会通过调整 Prompt 或者改进工具来修正问题。总的来说,自动化+人工的结合让评估既有广度又有深度。
5. 可观测性与日志调试:调试多智能体系统的困难之处在于它们的行为具有非确定性。每次运行可能都是不同的,而且涉及到很多的交互步骤。Anthropic 的方法是为系统环境添加详细地跟踪日志。这些跟踪日志方便开发者时候定位问题,进行分析;此外,思考模式下也有助于开发者们快速定位问题。
6. 用模型调试模型:如果说用模型评判输出质量是让模型来做裁判,那用模型来调试模型,就是让它们来做 debug。比如,将一个失败的 case 的日志和 Prompt 交给 Claude,问他“为什么这里 Lead Agent”没有找到明显的信息,模型可能会帮助你进行分析,给你一个分析报告。当然,最终需要人来确认并且验证这些分析。
将一个多智能体系统从实验室推向生产,存在许多工程上的挑战。
挑战一:高额 Token 成本
基本上所有的多智能体系统都会遇到这个问题。因为需要同时运行多个智能体,并且往往需要多轮对话和大量内容,这导致 Token 的消耗量陡增。根据 Anthropic 自己的数据显示,一个多智能体研究系统平均用掉的 Token 量是普通单智能体的 15 倍左右。这会给用户造成很大的经济压力。
Anthropic 的做法是:首先,挑选高价值场景。它们将 claude 的多智能体功能聚焦在价值足够高的问题上,比如商业情报、专业研究等,因为用户愿意为高质量答案付出更高成本。 对于简单问答,Claude仍使用单Agent模式,这样把宝贵的Token预算用在刀刃上。其次,提升模型效率。 Anthropic不断升级模型(如从Claude 3.7升级到Claude 4),因为更强的模型能在相同Token预算下完成更多任务。
挑战二:长期状态与错误恢复
多智能体系统因为运行时间长,经历的步骤多,中间任何一个步骤出现问题,都会毁掉整个过程。例如:一个Subagent 卡住或者工具调用失败,往往会使后续的流程都白费。
Anthropic 的做法是设计容错和恢复机制。 例如:在一个流程中,某个 Subagent 由于网络问题中止运转,Lead Agent 并不会简单放弃任务,而是收到一个错误信号提示,然后尝试调整计划或重试。这背后涉及到多智能体系统框架的支持:要保存每个智能体的重要状态,在必要时重启系统能够继续上下文,而不是一切归零。
挑战三:调试难度和可追踪性
前面其实提到过,多智能体系统之间的交互和决策具有不确定性,使得调试定位问题非常困难 。
Anthropic在生产环境中投入了大量工作以增强系统的可追踪性。他们实现了全面的运行跟踪日志,包括每个智能体的每次思考内容(隐式地,可以选择记录Extended Thinking输出)、使用了哪个工具、返回了什么结果、Lead Agent做了什么决定等。这些日志在生产中实时收集,以供线下分析。
当用户报告“Claude没找到显而易见的信息”时,开发者可以检索日志看看:是不是Agent用了不好的搜索词?是不是选错了来源?还是某个工具出错?事实证明,开启详细追踪后,大部分此类问题都能找到根源 。例如,有次Claude漏掉了一部分答案,日志显示它其实找到了但在综合时误判丢弃了——针对这种情况,团队后来调整了Prompt权重,让Lead Agent更重视全面性。这种数据驱动的调试极大提升了修复效率。
不仅如此,Anthropic还开发了高层监控指标来捕捉系统行为模式,如平均每次查询创建的Subagent 数量、平均每个Subagent 调用的工具次数等。这些指标如果出现异常暴增,往往预示有bug或Prompt问题,在用户发现之前开发者就能预警并介入处理。
挑战四:部署更新的复杂性
多智能体系统本质上是由大量Prompt、工具接口和执行逻辑组成的复杂网络,并且是高度有状态、长时间运行的。这给代码或Prompt的上线更新带来了巨大的挑战。 当我们更新系统时,可能有许多智能体正处于中间状态,不能简单进行重启 。
Anthropic为此采用了渐进式部署(rainbow deploy) 技术 。 简单来说,就是当发布新版本时,不会立刻把所有流量都切到新版本,而是让一部分新请求使用新版,老的仍用旧版,逐渐增加新版比例 。同时,已经在跑的老版本智能体继续跑完不受干扰。这类似于“彩虹”渐变,保证系统平滑过渡,避免中断正在进行的对话 。此外,在部署前团队会特别留意那些Prompt或代码的改动会如何影响智能体行为,通过模拟测试来验证不会导致新问题。总之,他们把部署看做一个需要精心策划的过程,以免“一刀切”更新导致用户的多轮对话过程被中断或行为骤变。
挑战五:同步架构的瓶颈
当前整个多智能体研究系统的 Lead Agent与Subagent 协调采取的是同步轮次的方式:Lead Agent一次发起一批Subagent,然后等待所有完成后再进行下一步 。这种做法的好处是简单,Lead Agent可以统一整合一批结果再决定后续动作。但缺点也明显:存在等待瓶颈。比如,如果有一个Subagent别慢,Lead Agent和其他 Subagent 都得干等。另外,Lead Agent在Subagent 执行期间无法介入指导,Subagent之间也不能互相协调 。整个系统实际上被分成了隔离的一轮轮。在一些任务中,这降低了效率和灵活性。
Anthropic已经意识到,异步执行也许是未来的发展方向:允许Lead Agent 不必等所有 Subagent 都结束就先处理部分结果,或者根据实时情况再派出新的Subagent ;Subagent 之间若能共享一些中间发现,可能少走重复路。当然,实现异步会大大增加协调难度,涉及并发管理、状态一致性、错误传播等复杂问题 。
Anthropic判断,随着模型能力增强,可以承担更复杂的长程任务时,异步架构带来的性能提升将值得那时去实现 。但在当前,他们权衡利弊选择了同步方案,并通过增加并行度尽可能降低等待影响。
挑战六:上下文和长对话管理
多智能体系统涉及超长的对话(动辄上百轮的工具交互),而大模型本身的上下文窗口是有限的。这带来了上下文管理挑战:如何不丢失关键信息,又避免超长上下文超出模型能力?
Anthropic的解决方案是引入智能的摘要与内存机制 。正如前面提到的,Lead Agent会在完成某阶段任务后,将当前进展和计划总结存储到Memory,然后开始新的阶段 。如果上下文长度接近极限,Lead Agent 就生成新的 Subagent,从干净上下文开始,同时通过Memory把必要的背景传递过去 。例如,当Lead Agent已经对某部分完成调查后,它可以让一个新的智能体在没有历史包袱的情况下继续下一个部分。这样,通过阶段性重置和记忆提取,他们避免了单个对话无限膨胀导致模型遗忘前面内容或截断。这种分布式上下文管理方式使Claude能够处理更长、更复杂的任务。同时也是对真实生产场景的考量:如果用户长时间与多智能体系统交互,必须保证上下文一致性和性能。
挑战七:结果传输的损耗
Anthropic注意到,在多层智能体传递信息的过程中,可能出现“传话游戏”效应:如果Subagent 找到一大段有用资料,但只能通过Lead Agent摘要转述给用户,可能信息有损,还浪费Token。
在生产中,他们引入了一种 Subagent 直接产出交付的机制。 具体而言,对于某些结构化输出(例如代码片段、长报告、数据表格),子代理可以直接把结果保存到共享的外部存储(比如文件系统或数据库),然后把引用指针给Lead Agent 。Lead Agent拿到指针后,可以将结果直接嵌入最终答案,或者提供给用户下载/查看 。
这样,避免了Lead Agent必须读一遍子代理长输出再复述,既提高了保真度又减少了Token开销 。 例如,一个代码生成的 Subagent 可以把代码写入文件,Lead Agent只需要简单描述结果并附上文件链接,而不用占用自己上下文重复代码内容。这种“旁路”传输方法在工程上提高了效率,也为多智能体协作提供了新的模式:专业子代理直接交付其专业产出。
通过以上种种措施,Anthropic克服了很多工程上的挑战,使得多智能体系统能够稳定、高效地运行在生产环境。这些经验表明,要让多智能体系统真正可用,除了让AI变聪明,还需要大量脚踏实地的工程工作:考虑资源和成本、建立健壮的运行机制、确保系统可维护可扩展等等。这些都是将原型转化为可靠产品的关键步骤。
好啦,今天的分享就先到这儿了~
像Anthropic 这类公司的博客强烈建议大家都去读一下原文,因为它们的文章中包含了它们大量的实践经验,以及对未来 AI 发展的思考和判断,这些无论是对企业的业务落地还是个人的 AI 素质提升,都具有很强的指导意义。
文章来自于“BubbleBrain”,作者“DylanDDeng”。
【开源免费】Browser-use 是一个用户AI代理直接可以控制浏览器的工具。它能够让AI 自动执行浏览器中的各种任务,如比较价格、添加购物车、回复各种社交媒体等。
项目地址:https://github.com/browser-use/browser-use
【开源免费】字节工作流产品扣子两大核心业务:Coze Studio(扣子开发平台)和 Coze Loop(扣子罗盘)全面开源,而且采用的是 Apache 2.0 许可证,支持商用!
项目地址:https://github.com/coze-dev/coze-studio
【开源免费】n8n是一个可以自定义工作流的AI项目,它提供了200个工作节点来帮助用户实现工作流的编排。
项目地址:https://github.com/n8n-io/n8n
在线使用:https://n8n.io/(付费)
【开源免费】DB-GPT是一个AI原生数据应用开发框架,它提供开发多模型管理(SMMF)、Text2SQL效果优化、RAG框架以及优化、Multi-Agents框架协作、AWEL(智能体工作流编排)等多种技术能力,让围绕数据库构建大模型应用更简单、更方便。
项目地址:https://github.com/eosphoros-ai/DB-GPT?tab=readme-ov-file
【开源免费】VectorVein是一个不需要任何编程基础,任何人都能用的AI工作流编辑工具。你可以将复杂的工作分解成多个步骤,并通过VectorVein固定并让AI依次完成。VectorVein是字节coze的平替产品。
项目地址:https://github.com/AndersonBY/vector-vein?tab=readme-ov-file
在线使用:https://vectorvein.ai/(付费)
【开源免费】AutoGPT是一个允许用户创建和运行智能体的(AI Agents)项目。用户创建的智能体能够自动执行各种任务,从而让AI有步骤的去解决实际问题。
项目地址:https://github.com/Significant-Gravitas/AutoGPT
【开源免费】MetaGPT是一个“软件开发公司”的智能体项目,只需要输入一句话的老板需求,MetaGPT即可输出用户故事 / 竞品分析 / 需求 / 数据结构 / APIs / 文件等软件开发的相关内容。MetaGPT内置了各种AI角色,包括产品经理 / 架构师 / 项目经理 / 工程师,MetaGPT提供了一个精心调配的软件公司研发全过程的SOP。
项目地址:https://github.com/geekan/MetaGPT/blob/main/docs/README_CN.md
【开源免费】LangGPT 是一个通过结构化和模板化的方法,编写高质量的AI提示词的开源项目。它可以让任何非专业的用户轻松创建高水平的提示词,进而高质量的帮助用户通过AI解决问题。
项目地址:https://github.com/langgptai/LangGPT/blob/main/README_zh.md
在线使用:https://kimi.moonshot.cn/kimiplus/conpg00t7lagbbsfqkq0